Preliminary approach for the surface electromyographical evaluation of the oral phase of swallowing
BACKGROUND:
Swallowing is a muscular activity that occurs both after mastication and spontaneously as a result of saliva accumulation. Spontaneous saliva swallowing occurs about every 2 minutes. Comprehension of its functional mechanisms is relevant to assess their modification in clinical situations. A standardised surface electromyographical (ssEMG) protocol for the evaluation of this muscle activity is lacking.
ACHIEVMENTS:
Aims of the present study are:
- to determine the reproducibility of a ssEMG protocol for the evaluation of the oral phase of saliva swallowing and
- to evaluate the activity of masseter (MM), anterior temporalis (TA), submental muscles (SM) to draw a reference model of swallowing.
METHODS:
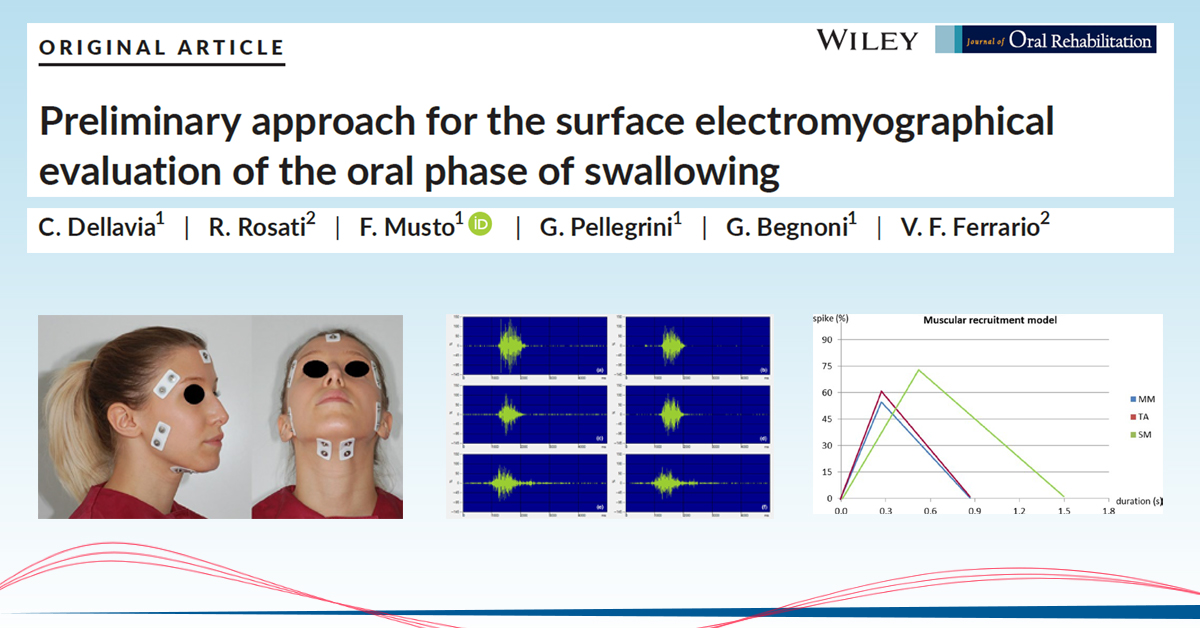
Standardised surface electromyographical activity of MM, TA and SM during swallowing of saliva spontaneously accumulated was recorded in 20 healthy participants. Functional indexes including symmetry (POC), recruitment (Impact), duration of activation of each couple of muscles and of the whole exercise, position, intensity of the spike were computed. Inter- and intra-appointment reliabilities were assessed and method errors calculated. Descriptive statistics, sex- and muscles-related comparisons were carried out.
RESULTS:
Standardised surface electromyographical assessment of MM, TA and SM muscles was reliable. A high inter-individual variability was found. Percentage overlapping coefficient (POC) values were close to 80% for TA and SM, higher than for MM (P < .001). Impact values ranged between 16.4% and 30.7%, and differences were found between muscles (P < .001). The global muscle activity during swallowing lasted between 1.5 and 1.8 seconds. For each couple of muscles, the duration of activation ranged between 0.7 and 1.6 seconds and muscles-related differences were found (P < .001). The spike of activation for each couple of muscle ranged between 35.7% and 44.2% of the duration.
CONCLUSIONS:
The protocol was reliable and intra-participants repeatable measures can be carried out. Due to the high inter-participants variability, further analyses are needed to draw a model of muscular activity.
KEY WORDS:
submental muscles, surface electromyography, swallowing
This approach then opens up the possibility of introducing a new method of functional analysis in the daily clinic to study the phenomenon of swallowing.