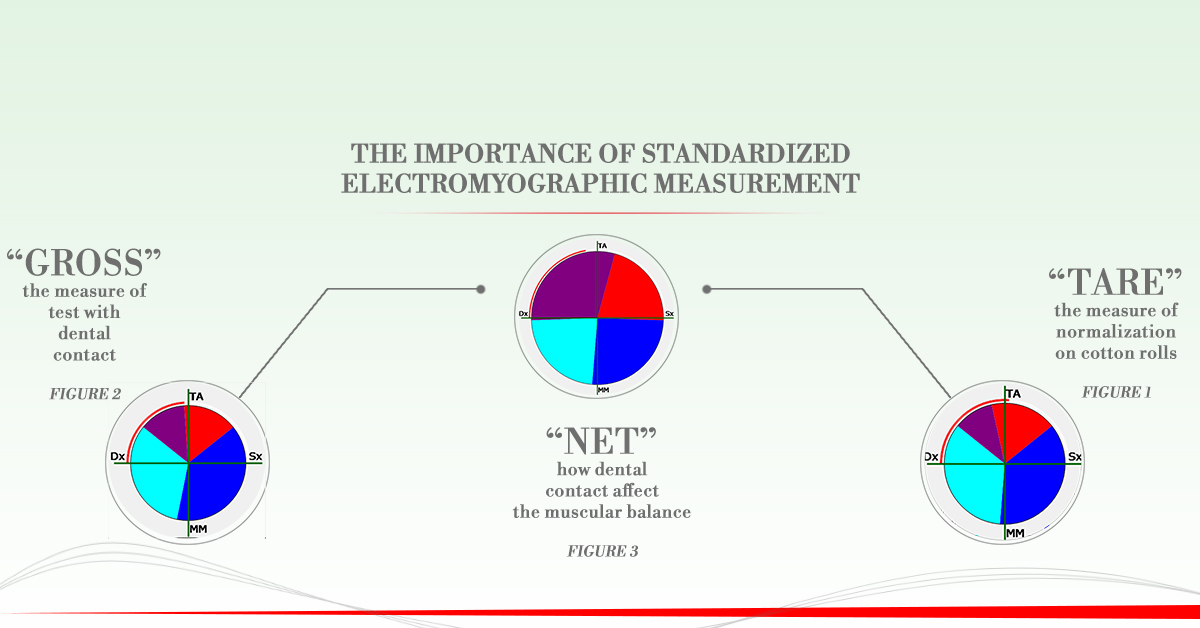
The importance of normalizing the electromyographic measurement
Cotton rolls pie chart
This graph shows the data related to the standardization measurement performed with the cotton rolls interposed between the two arches (with reduced dento-periodontal proprioception). It is possible to identify 4 quadrants related to 4 specific muscles according to the protocol in execution (Figure 1).
A specific muscle is associated with each color. The size of each slice is proportional to the electrical activity generated by that muscle compared to the others taken into consideration within the same graph. The relative dimensions of the cake slices are specific to each patient and are due to the muscular balances developed by that particular patient. All subsequent tests will be normalized on this measurement.
μV pie chart
This graph shows the data related to the measurement performed with the teeth in contact (or prostheses, plates, occlusal, bite, etc.) (Figure 2).
As in the Cotton rolls pie chart, a specific muscle is associated with each color and the size of the pie slice is proportional to the activity of that muscle compared to the others examined.
Percent pie chart
In this graph (Figure 3) the result of the overlapping of the Cotton rolls and μV pie charts is displayed. It expresses the standardized differential activity, attributable to dental contact.
Scientific studies have shown that young healthy subjects, without functional and morphological alterations, exercise similar muscular performances by tightening their teeth in maximum intercuspation or with cotton rolls between the arches. In this condition the percent pie chart will represent 4 equal slices. When this does not happen it means that in maximum intercuspation the subject has established a muscle recruitment different from that performed with the cotton rolls and so it is advisable to investigate the possible causes.
The normalized quantification of the dento-periodontal proprioceptive component thus extrapolated has two main advantages:
- it reduces the variability of the electromyographic examination by increasing its repeatability in subsequent sessions by eliminating the main bias of this discipline that is the repeatability;
- it allows to isolate a single factor (dento-periodontal proprioception) allowing to understand the consequences in the coordination of the chewing muscles and the neck.